26
Jan
Rubber materials are widely used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, rail transit, and industrial equipment industries due to their excellent elasticity, wear resistance, vibration damping, and sealing performance. In the manufacturing and post-processing of rubber components, grinding is a critical process used for surface finishing, dimensional correction, and improvement of surface quality.
Compared with metals, ceramics, and engineering plastics, rubber materials exhibit high elasticity, low thermal conductivity, and strong sensitivity to heat. These characteristics make rubber grinding prone to issues such as surface burning, tearing, thermal deformation, and dimensional instability. Therefore, rubber grinding requires specially optimized grinding tools, process parameters, and cooling methods.


(1) Abrasive and Bond Types
Common grinding wheels for rubber processing include diamond wheels, CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) wheels, and resin-bond grinding wheels:



(2) Grinding Wheel Types
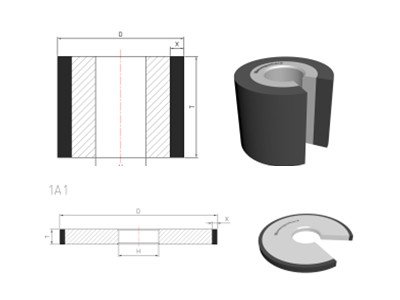
According to the structure and application of rubber components, different grinding wheel shapes can be selected:
(1) Cutting Speed
Due to the poor thermal conductivity of rubber, excessive heat can easily accumulate during grinding. Therefore, the grinding speed for rubber materials is generally lower than that used for metal grinding, effectively reducing softening, burning, and surface melting.
(2) Feed Rate
The feed rate must be carefully controlled:
Trial grinding is typically required to determine the optimal feed parameters.
(3) Cooling Method
Cooling plays a crucial role in rubber grinding. Proper cooling can:
Water-based coolants or emulsified coolants with functional additives are commonly used.
(1) Rough Grinding and Finish Grinding
Rubber grinding usually adopts a staged process:
Proper allocation of grinding allowance effectively reduces the risk of surface damage.
(2) Post-Grinding Surface Treatment
For high-end applications, additional processes such as polishing, coating, or functional surface treatment may be applied after grinding to further enhance surface performance and service life.
Background:
During tire manufacturing, precision grinding of the inner surface is required to ensure accurate fit and airtight sealing between the tire and the wheel rim.
Technical Implementation:
Results:
After precision grinding, the inner surface of the tire achieved excellent smoothness and dimensional stability, significantly improving rim fit, reducing air leakage and vibration, and enhancing driving safety and comfort.
Background:
Rubber seals used in aircraft engines require extremely high dimensional accuracy and surface integrity to ensure reliable sealing performance under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.
Technical Implementation:
Results:
The ground seals exhibited smooth, defect-free surfaces and stable dimensional accuracy, significantly enhancing sealing performance and ensuring the safe and efficient operation of aircraft engines.
Rubber grinding plays a vital role in modern manufacturing. From automotive tires to aircraft engine seals, proper selection of grinding wheels and precise control of process parameters directly affect product quality, performance, and reliability.
With the advancement of intelligent manufacturing and green processing technologies, rubber grinding solutions will continue to evolve, providing more efficient and reliable support for automotive, aerospace, and high-end industrial applications.







