30
Jan
The dicing blade used in wafer cutting is a missing link in China’s semiconductor packaging industry chain, which has been dependent on import for a very long time. No matter from the perspective of national development strategy or national security strategy, this gap must be filled as soon as possible. We should commit to building a production base for wafer cutters in China, realizing the localization of wafer blades, and fully meeting the urgent needs of China’s integrated circuit, discrete devices, LED and other industries for dicing blades.
What is Wafer Dicing Blade?
In the early stage of semiconductor wafer packaging, dicing blade is an important tool used to cut wafers and manufacture chips. It has a direct impact on the quality and life of chips. The application of the dicing blade in semiconductor packaging process is shown in the following figure:
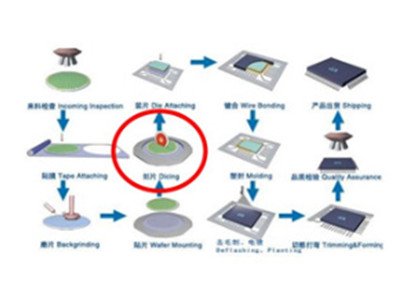
Wafer Dicing
Dicing is commonly used to separate optical components or electronics imaged onto wafers. The substrates can be waxed onto hard mounts to minimize chipping.

What is Wafer Dicing?
The wafer dicing process separates small blocks of semiconducting material (known as dice) from a semiconductor wafer. Depending on the application’s needs, the dicing process may involve wafer scribing, through cutting, or wax mounting. The wafer is sawed in the extra spaces between dice to separate them.
Usually, manufacturers mount wafers onto tape to improve their backside support. Once the wafer has been mounted, it’s loaded into a cassette and then into the actual dicing mechanism, which cuts the wafer into individual dice.
The dicing mechanism contains an abrasive blade that it rotates with a spindle at high speeds (usually 30,000–60,000 rpm).
Blades used for this purpose comprise diamond grit embedded into an electroplated nickel matrix. Because these blades are so strong, they easily crush wafers, and any debris that it creates can be removed while the machine works.
The blade moves between active areas of the dice through dedicated lines known as streets. This creates a groove in the substrate material.

With the miniaturization, high capacity and high efficiency of chips, the structure of chips becomes more and more complex, and the effective space between chips becomes smaller and smaller, so the space of cutting becomes narrower and narrower. This is more and more demanding for precision wafer dicing blades.
At present, there are two ways to cut wafers: one is laser cutting, the other is mechanical cutting, that is, dicing blade cutting. The latter is currently the main force in wafer cutting. The reason for this is that (1) high-power laser cutting can’t use lest produce heat affected zone (HAZ) chip, (2) laser cutting equipment is very expensive (generally in $1 million/table above), (3) laser cutting can’t do it all at one time (because the HAZ problem), and thus a second cut still should use dicing blade to finishing, so dicing blade is one of the indispensable material in semiconductor packaging technology.
Most of the silicon substrate integrated circuits and device products need to be cut with a dicing blade when they are packaged. Global economic and semiconductor industry statistics for the past 25 years show that the annual growth rate of the semiconductor integrated circuits and devices market is in line with the annual growth rate of global GDP, so the demand for dicing blades is also increasing year by year.
Analysis on The Market of Dicing Blades:
At present, there are about 10 major manufacturers in the global dicing blades market, leading manufacturers in the industry are DISCO in Japan, ADT in Israel, K&S in the United States, etc. Currently, the domestic annual demand of dicing blades is 6-8 million pieces. According to the estimated price of 160 yuan/piece, the market scale is about 1-1.5 billion yuan. DISCO is basically a monopoly of the domestic dicing blades market. The technical barrier is product’s yield, which, according to DISCO’s annual report, is as high as 52% gross margin.
DISCO was founded in 1937 and is headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. Mainly for the manufacture and sales of precision processing equipment and tools, including dicing machine, grinding machine, Surface Planer, polishing machine, etc. The leasing of precision processing equipment and the sale of used equipment, as well as the processing services of precision parts; Mainly used in semiconductors, electronics and construction industry.

Advanced Dicing Technologies (ADT), Israel specializes in semiconductor wafer cutting (dicing), chip packaging cutting (dicing) and microelectronic component related systems, process development and blade manufacturing (Hubless Blades), providing professional dicing and slotting services for electronic and optical devices. In 2003, the investor acquired Kulicke&Soffa (K&S) cutting equipment (dicing machine) and blade manufacturing (Hubless Blades (Sofas) sales department of Kulicke&Soffa Semiconductor Limited (K&S) and established Advanced Dicing Technologies (ADT) Israel. ADT’s corporate headquarters, research and development facilities and two production plants are located in Israel. The company employs about 160 professionals.








